Health Insurance Insurance Types

The world of health insurance is vast and complex, offering a myriad of options to cater to the diverse needs of individuals and families. Understanding the different types of health insurance plans is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare coverage. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the various health insurance types, exploring their features, benefits, and suitability for different scenarios.
Understanding Health Insurance Fundamentals
Health insurance is a safeguard against the potentially high costs of medical care. It provides financial protection by covering a range of healthcare services, from routine check-ups and preventive care to more complex procedures and treatments. With the right health insurance plan, individuals can access quality healthcare without incurring significant out-of-pocket expenses.
The fundamental concept behind health insurance is risk sharing. When a large group of people pool their resources to cover healthcare costs, the financial burden is distributed, making healthcare more affordable and accessible. Insurance companies calculate premiums based on various factors, including age, location, health status, and the type of coverage chosen.
Exploring the Diverse Landscape of Health Insurance Types

The health insurance market offers a wide array of plan types, each designed to cater to specific demographics and healthcare needs. Here, we dissect the most common types of health insurance plans and their unique features.
1. Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance plans are purchased directly from insurance companies or through brokers. These plans offer a wide range of coverage options, from basic to comprehensive, allowing individuals to choose the level of coverage that aligns with their budget and healthcare requirements.
Key Features:
- Flexible coverage options: Private health insurance plans often provide a menu of coverage levels, allowing individuals to customize their plan to their specific needs.
- Network of providers: These plans typically have a network of preferred healthcare providers, offering discounted rates for in-network services.
- Out-of-pocket costs: Private insurance plans may have deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, which are the individual's responsibility.
2. Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Many employers offer health insurance plans as part of their employee benefits package. These plans are often more affordable for employees, as the employer typically contributes a portion of the premium.
Key Features:
- Group coverage: Employer-sponsored plans provide coverage for a group of individuals, which can include employees and their families.
- Premium contributions: Employers often subsidize a significant portion of the premium, making healthcare more accessible for employees.
- Network restrictions: These plans may have limited provider networks, which can impact the choice of healthcare professionals.
3. Government-Sponsored Health Insurance
Government-sponsored health insurance programs are designed to provide coverage for specific populations, such as low-income individuals, seniors, and people with disabilities. These programs are funded and managed by federal, state, or local governments.
Key Features:
- Income-based eligibility: Government-sponsored programs often have income requirements, ensuring that coverage is accessible to those who need it most.
- Comprehensive coverage: These plans typically offer a wide range of healthcare services, including preventive care, prescription medications, and specialist visits.
- No or low out-of-pocket costs: Government-sponsored plans often have minimal or no deductibles, copayments, or coinsurance.
4. Short-Term Health Insurance
Short-term health insurance plans are designed to provide temporary coverage for individuals who are between jobs, waiting for other coverage to begin, or facing a gap in their healthcare coverage.
Key Features:
- Limited duration: Short-term plans typically last for a set period, usually ranging from a few months to a year.
- Limited coverage: These plans often have restrictions on pre-existing conditions and may not cover certain services, such as maternity care or mental health services.
- Lower premiums: Short-term plans are generally more affordable than long-term plans, but they may have higher out-of-pocket costs.
5. High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
High-deductible health plans are a type of insurance plan that combines a high annual deductible with a health savings account (HSA). HDHPs are designed to encourage individuals to take a more active role in their healthcare decisions.
Key Features:
- High deductible: HDHPs have a higher annual deductible than traditional plans, meaning individuals must pay more out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in.
- Health Savings Account (HSA): An HSA is a tax-advantaged savings account that can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses. Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified expenses are tax-free.
- Lower premiums: HDHPs often have lower premiums compared to traditional plans, making them an attractive option for individuals who prioritize saving for future healthcare costs.
6. Catastrophic Health Insurance
Catastrophic health insurance plans are designed to provide coverage for major, unexpected medical events. These plans typically have low premiums but high deductibles, making them suitable for individuals who are healthy and want protection against significant financial losses.
Key Features:
- Limited coverage: Catastrophic plans often have minimal benefits and may only cover essential health benefits, such as emergency care and hospitalization.
- High deductible: These plans have a very high annual deductible, which must be met before insurance coverage begins.
- Preventive care: Despite their limited coverage, catastrophic plans often include some preventive services, such as vaccinations and screenings, at no cost to the individual.
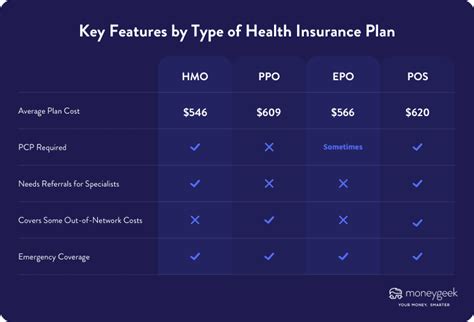
7. Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) are a type of managed care plan that emphasizes preventive care and coordinated services. HMOs typically have a network of healthcare providers, and members must choose a primary care physician (PCP) within that network.
Key Features:
- Primary care physician: Members of an HMO plan must select a PCP, who acts as their primary point of contact for healthcare services.
- Network restrictions: HMO plans have a limited network of providers, and out-of-network services may not be covered or may require prior authorization.
- Preventive care focus: HMOs promote preventive care and wellness, often covering annual check-ups, screenings, and immunizations at no additional cost.
8. Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing members to choose their healthcare providers both inside and outside the plan's network.
Key Features:
- Network of providers: PPOs have a network of preferred providers, but members can also seek care from out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
- Out-of-network coverage: While in-network services are generally more affordable, PPO plans also cover out-of-network care, albeit with higher out-of-pocket expenses.
- Referrals not required: Unlike HMOs, PPO plans do not typically require referrals from a primary care physician to see specialists.
9. Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs) are similar to PPOs in that they offer a network of preferred providers. However, EPOs do not cover out-of-network services, making them a more cost-effective option for those who are comfortable with the plan's network.
Key Features:
- Network of providers: EPO plans have a network of healthcare providers, and members must use in-network services to receive coverage.
- No out-of-network coverage: Unlike PPOs, EPOs do not cover out-of-network services, which means members may have limited choices for healthcare providers.
- Cost savings: By limiting coverage to in-network providers, EPO plans can offer lower premiums and reduced out-of-pocket costs.
10. Point of Service (POS) Plans
Point of Service (POS) plans combine elements of both HMOs and PPOs. Members of a POS plan typically choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the plan's network, but they also have the option to seek care from out-of-network providers, similar to PPOs.
Key Features:
- Primary care physician: Like HMOs, POS plans require members to select a PCP for their primary healthcare needs.
- Network of providers: POS plans have a network of preferred providers, and in-network services are generally more affordable.
- Out-of-network coverage: Unlike HMOs, POS plans cover out-of-network services, but members may need to obtain a referral from their PCP and pay higher out-of-pocket costs.
Comparative Analysis: Choosing the Right Health Insurance Plan
Selecting the right health insurance plan involves careful consideration of your individual needs and circumstances. Here's a comparative analysis to help you make an informed decision.
| Plan Type | Premium Costs | Out-of-Pocket Expenses | Network Flexibility | Coverage Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private Health Insurance | Varies, customizable | Deductibles, copayments, coinsurance | Flexible, depending on plan | Wide range of options |
| Employer-Sponsored | Often subsidized by employer | May have copayments or coinsurance | Limited to employer's network | Varies, group-based |
| Government-Sponsored | Little to no cost | Minimal or no out-of-pocket costs | Network restrictions may apply | Comprehensive, income-based eligibility |
| Short-Term | Affordable, lower premiums | Higher out-of-pocket costs | Limited, may have restrictions | Basic, temporary coverage |
| HDHPs | Lower premiums | High deductible, HSA-eligible | Flexible, depending on plan | Comprehensive, with HSA savings |
| Catastrophic | Low premiums | Very high deductible | Limited, may have restrictions | Essential health benefits |
| HMO | Varies, often affordable | May have copayments | Network-based, restricted | Preventive care focus |
| PPO | Higher premiums | Flexible, depending on network | Flexible, in and out of network | Wide range of coverage |
| EPO | Affordable | Lower out-of-pocket costs | Limited to in-network providers | Cost-effective, network-based |
| POS | Varies | Flexible, in and out of network | Flexible, with PCP referrals | Combines HMO and PPO features |

When choosing a health insurance plan, consider your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences for flexibility and coverage. It's essential to carefully review the plan's benefits, network of providers, and potential out-of-pocket costs to ensure it aligns with your individual circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between an HMO and a PPO plan?
+HMOs typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within their network and usually require referrals for specialist visits. PPOs, on the other hand, offer more flexibility, allowing members to see any in-network provider without a referral and also cover out-of-network services at a higher cost.
Are government-sponsored health insurance plans free?
+Government-sponsored plans, such as Medicaid and Medicare, are not entirely free. While they are heavily subsidized by the government, individuals may still have to pay premiums, deductibles, or copayments, depending on their income and the specific program.
Can I change my health insurance plan during the year?
+In most cases, you can only change your health insurance plan during the open enrollment period, which is a set time each year when individuals can enroll in or switch plans. However, certain life events, such as marriage, divorce, or the birth of a child, may qualify you for a special enrollment period outside of the open enrollment window.
What is the advantage of a High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP)?
+HDHPs offer the advantage of lower premiums and the opportunity to save for future healthcare costs through a Health Savings Account (HSA). This plan type is ideal for individuals who prioritize saving for healthcare expenses and are willing to pay more out-of-pocket in the short term.



