Insurance Hmo Vs Ppo
The healthcare industry offers a myriad of options for individuals and families to secure their health and financial well-being. Among these options are Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), two distinct types of health insurance plans that cater to different preferences and needs. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of HMOs and PPOs, shedding light on their key differences, benefits, and considerations to help you make an informed decision when choosing a health insurance plan.
Understanding Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)

Health Maintenance Organizations, or HMOs, are a popular choice for those seeking cost-effective and structured healthcare coverage. HMOs are characterized by a network of contracted healthcare providers, including doctors, specialists, and hospitals, who agree to offer services at negotiated rates. This network is carefully curated to provide a comprehensive range of healthcare services to HMO members.
Key Features of HMOs
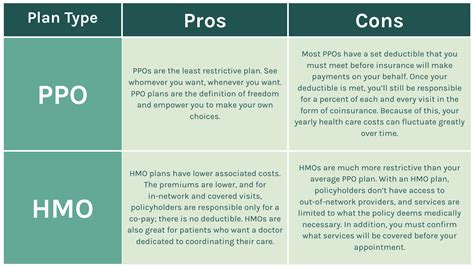
- Network-based Care: HMO plans require members to select a primary care physician (PCP) from within the HMO network. This PCP acts as a gatekeeper, coordinating all healthcare services and referrals to specialists.
- Cost-effectiveness: HMOs are known for their affordable premiums and low out-of-pocket costs. They typically have lower deductibles and copayments compared to other plan types.
- Preventive Care Emphasis: HMOs often place a strong emphasis on preventive care, offering a wide range of preventive services at little to no cost. This includes annual check-ups, immunizations, and screenings.
- HMO Exclusive Networks: Members are generally required to stay within the HMO network for services. Out-of-network care is typically not covered or incurs higher out-of-pocket expenses.
| Feature | HMO |
|---|---|
| Primary Care Physician (PCP) | Required; acts as a gatekeeper |
| Network Size | Smaller, carefully selected network |
| Cost Structure | Lower premiums, deductibles, and copays |
| Referrals | Required for specialist visits |
| Out-of-Network Coverage | Limited or no coverage |

Pros and Cons of HMOs
Pros:
- Affordable premiums and low out-of-pocket costs.
- Emphasis on preventive care and wellness.
- Coordinated care through a primary care physician.
- Ideal for those who prefer a structured healthcare approach.
Cons:
- Limited choice of providers within the network.
- Referrals are required for specialist visits.
- Out-of-network care is generally not covered.
- May not be suitable for those who prefer flexibility in provider choice.
Exploring Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)

Preferred Provider Organizations, or PPOs, offer a more flexible and comprehensive healthcare coverage option compared to HMOs. PPOs maintain a network of contracted healthcare providers, similar to HMOs, but with a broader range of options. PPO members have the freedom to choose from both in-network and out-of-network providers, although using in-network providers typically results in lower costs.
Key Features of PPOs
- Provider Flexibility: PPOs allow members to choose any healthcare provider, whether in-network or out-of-network. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for those who have established relationships with specific doctors or specialists.
- Co-pays and Deductibles: PPOs generally have higher premiums and deductibles compared to HMOs. However, the trade-off is greater flexibility and control over healthcare choices.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: PPOs offer some coverage for out-of-network services, although at a higher cost. This coverage is particularly useful for individuals who require specialized care or have unique healthcare needs.
| Feature | PPO |
|---|---|
| Primary Care Physician (PCP) | Optional; members can choose specialists directly |
| Network Size | Larger network with more provider options |
| Cost Structure | Higher premiums and deductibles; lower copays |
| Referrals | Not required; direct access to specialists |
| Out-of-Network Coverage | Partial coverage; higher out-of-pocket costs |
Pros and Cons of PPOs
Pros:
- Flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
- Direct access to specialists without referrals.
- Partial coverage for out-of-network services.
- Suitable for those with unique healthcare needs or established provider relationships.
Cons:
- Higher premiums and deductibles.
- Increased out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care.
- May not be as cost-effective for those with minimal healthcare needs.
Comparing HMOs and PPOs: A Side-by-Side Analysis
When deciding between an HMO and a PPO, it's essential to consider your personal healthcare needs, preferences, and budget. Here's a detailed comparison to help you make an informed decision:
Cost Comparison
HMOs generally offer more affordable premiums and lower out-of-pocket costs due to their structured network and emphasis on preventive care. On the other hand, PPOs typically have higher premiums and deductibles, reflecting their broader network and greater flexibility.
Provider Network and Flexibility
HMOs operate with a smaller, curated network of providers, requiring members to choose a primary care physician and obtain referrals for specialist visits. PPOs, in contrast, provide a larger network with more provider options, allowing members to choose any healthcare provider, whether in-network or out-of-network.
Preventive Care Emphasis
HMOs place a strong focus on preventive care, often offering a wide range of preventive services at little to no cost. PPOs also emphasize preventive care, but to a lesser extent, as their primary focus is on providing flexible healthcare options.
Specialty Care and Out-of-Network Coverage
HMOs generally do not provide coverage for out-of-network care, making it a less suitable option for individuals with specific healthcare needs or those who prefer a particular provider outside the HMO network. PPOs, however, offer partial coverage for out-of-network services, making them a more viable choice for those seeking specialty care or requiring unique healthcare services.
Coordination of Care
HMOs emphasize coordinated care through a primary care physician, who acts as a gatekeeper for all healthcare services. This structure ensures that members receive appropriate referrals and specialized care. PPOs, on the other hand, allow direct access to specialists without referrals, providing greater autonomy in managing healthcare decisions.
Choosing the Right Plan: Considerations and Recommendations
Selecting the right health insurance plan depends on various factors, including your healthcare needs, budget, and personal preferences. Here are some considerations to guide your decision-making process:
Assess Your Healthcare Needs
Evaluate your current and potential future healthcare needs. Consider any chronic conditions, specialized care requirements, or unique healthcare circumstances. If you anticipate needing specialized care or have established relationships with specific providers, a PPO plan may be more suitable.
Evaluate Your Budget
Take into account your financial situation and the affordability of different plan options. HMOs are generally more cost-effective with lower premiums and out-of-pocket expenses. PPOs, while offering greater flexibility, come with higher premiums and deductibles.
Consider Provider Networks
Review the provider networks of both HMO and PPO plans. Ensure that your preferred doctors, specialists, and hospitals are included in the network. If you have a strong preference for specific providers, a PPO plan may provide the necessary flexibility.
Prioritize Preventive Care
If preventive care and wellness are high priorities for you, an HMO plan may be the ideal choice. HMOs typically offer a comprehensive range of preventive services at little to no cost, encouraging members to stay proactive about their health.
Seek Professional Guidance
Consult with healthcare professionals, insurance brokers, or financial advisors to gain expert insights and recommendations tailored to your specific needs and circumstances. They can provide valuable advice and help you navigate the complexities of health insurance plans.
Can I switch between HMO and PPO plans annually or more frequently?
+Switching between HMO and PPO plans typically occurs during the annual open enrollment period or when experiencing a qualifying life event, such as a job change or marriage. It's important to review the plan options carefully during these periods to ensure a smooth transition.
Do HMOs and PPOs cover pre-existing conditions?
+Yes, both HMOs and PPOs are required by law to cover pre-existing conditions without any waiting periods or exclusions. This ensures that individuals with existing health conditions have access to necessary healthcare services without discrimination.
Are there any age restrictions for HMO and PPO plans?
+No, HMO and PPO plans are available to individuals of all ages, including children and seniors. The plan options and coverage may vary based on age, but there are no blanket restrictions based solely on age.
Choosing between an HMO and a PPO plan involves a careful evaluation of your healthcare needs, budget, and personal preferences. Both plan types have their unique advantages and considerations, and understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision. By considering the factors outlined in this guide, you can select the health insurance plan that best aligns with your priorities and ensures your health and financial well-being.



