Obama Care Health Insurance
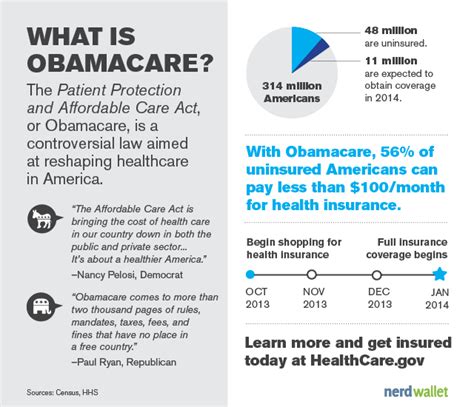
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, commonly known as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or ObamaCare, is a landmark legislation in the United States that aimed to reform the healthcare system and provide affordable, quality health insurance to millions of Americans. Signed into law in 2010, ObamaCare has had a significant impact on the healthcare landscape and continues to shape the way healthcare is delivered and accessed.
Understanding ObamaCare: A Comprehensive Overview

ObamaCare, a key initiative of former President Barack Obama, was designed to address the shortcomings of the existing healthcare system and make healthcare more accessible and affordable for all Americans. The law introduced several key provisions and reforms that have reshaped the healthcare industry.
Key Provisions of ObamaCare
- Individual Mandate: One of the most controversial aspects of ObamaCare was the individual mandate, which required all Americans to have health insurance or face a penalty. This mandate aimed to encourage a broader pool of insured individuals, reducing the risk for insurance companies and potentially lowering costs.
- Health Insurance Marketplaces: ObamaCare established state-based Health Insurance Marketplaces (also known as Exchanges) where individuals and small businesses could shop for and compare health insurance plans. These marketplaces aimed to increase competition and make it easier for consumers to find suitable coverage.
- Essential Health Benefits: The law defined a set of essential health benefits that all insurance plans sold on the marketplaces must cover. These benefits include ambulatory patient services, emergency services, hospitalization, maternity and newborn care, mental health and substance use disorder services, prescription drugs, rehabilitative and habilitative services, and more.
- Pre-existing Condition Coverage: Prior to ObamaCare, many individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or cancer, were denied coverage or faced high premiums. The law prohibited insurance companies from denying coverage or charging more based on pre-existing conditions, ensuring that all Americans had access to affordable healthcare.
- Medicaid Expansion: ObamaCare expanded Medicaid eligibility to include more low-income individuals and families. This expansion aimed to provide coverage to those who couldn’t afford private insurance, reducing the number of uninsured Americans.
Impact and Benefits of ObamaCare
ObamaCare has had a profound impact on the healthcare system and the lives of millions of Americans. Here are some key benefits and outcomes:
- A significant decrease in the uninsured rate: According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the uninsured rate dropped from 16.0% in 2010 to 8.5% in 2019, a decrease of over 7.5%. This translates to millions of previously uninsured Americans gaining access to healthcare.
- Improved access to preventive care: ObamaCare emphasized the importance of preventive services, making them more affordable and accessible. This has led to an increase in screenings, vaccinations, and early detection of health issues, potentially reducing long-term healthcare costs.
- Protection for those with pre-existing conditions: Prior to ObamaCare, individuals with pre-existing conditions often faced significant barriers to obtaining insurance. The law’s protections have ensured that millions of Americans with pre-existing conditions can access affordable coverage, providing peace of mind and improved health outcomes.
- Young adults benefiting from parental coverage: ObamaCare allowed young adults to remain on their parents’ health insurance plans until they turned 26, providing a safety net for this vulnerable population. This provision has helped ensure continuous coverage for young adults, who may face challenges in finding and affording insurance on their own.
- Enhanced consumer protections: The law introduced several consumer protections, including prohibiting lifetime and annual limits on coverage, requiring coverage for certain preventive services without cost-sharing, and ensuring that insurance companies spend a certain percentage of premiums on healthcare services rather than administrative costs.
Challenges and Controversies
While ObamaCare has brought about significant improvements, it has also faced challenges and controversies:
- Legal Battles: The law has been the subject of numerous legal challenges, with critics arguing that the individual mandate is unconstitutional. The Supreme Court has upheld the law twice, but these challenges have created uncertainty and impacted the implementation of ObamaCare.
- Marketplace Stability: The Health Insurance Marketplaces have faced challenges in maintaining a stable and competitive environment. Insurers have exited certain markets, and premium increases have been a concern in some areas, leading to calls for further reforms.
- Political Opposition: ObamaCare has been a highly politicized issue, with Republicans and Democrats holding differing views on the law. Political opposition has impacted the implementation and expansion of the law, leading to a patchwork of state-level approaches to healthcare reform.
Future of ObamaCare
The future of ObamaCare remains uncertain, as it continues to be a topic of political debate and legal scrutiny. However, the law has already made significant strides in improving access to healthcare and protecting consumers. Here are some potential future implications:
- State-Level Innovations: Some states have taken the lead in implementing and expanding healthcare reforms beyond the federal level. These state-level innovations, such as Medicaid expansion and state-based marketplaces, could serve as models for further improvements.
- Biden Administration’s Approach: The Biden administration has expressed support for ObamaCare and has taken steps to strengthen the law. This includes expanding access to Medicaid, improving affordability, and addressing gaps in coverage. The administration’s policies could shape the future of healthcare reform.
- Healthcare Cost Containment: Containing healthcare costs remains a critical challenge. Future reforms may focus on addressing the root causes of rising costs, such as improving healthcare delivery systems, enhancing value-based care, and incentivizing preventive services.
- Increased Emphasis on Telehealth: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telehealth services, and this trend is expected to continue. Telehealth can improve access to healthcare, especially in rural areas, and reduce costs associated with in-person visits. Future reforms may further integrate telehealth into the healthcare system.
Conclusion
ObamaCare, despite its challenges and controversies, has played a pivotal role in reshaping the U.S. healthcare system. It has expanded access to healthcare, protected consumers, and brought about much-needed reforms. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, ObamaCare’s legacy and impact will continue to shape future policies and innovations. Understanding the intricacies of this legislation is crucial for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals seeking affordable, quality healthcare.
What is the individual mandate in ObamaCare, and why was it controversial?
+The individual mandate in ObamaCare required all Americans to have health insurance or pay a penalty. This provision was controversial as critics argued that it infringed on individual liberties and mandated the purchase of a private good. However, supporters of the mandate believed it was necessary to ensure a broad pool of insured individuals, which could help control costs.
How has ObamaCare impacted the uninsured rate in the United States?
+ObamaCare has significantly reduced the uninsured rate in the United States. According to data, the uninsured rate dropped from 16.0% in 2010 to 8.5% in 2019, a decrease of over 7.5%. This means millions of previously uninsured Americans now have access to healthcare.
What are some of the key consumer protections introduced by ObamaCare?
+ObamaCare introduced several consumer protections, including prohibiting insurance companies from denying coverage based on pre-existing conditions, eliminating lifetime and annual limits on coverage, requiring coverage for certain preventive services without cost-sharing, and ensuring that a certain percentage of premiums are spent on healthcare services.



