Understanding The Penis

The penis is a fascinating and complex organ, often surrounded by curiosity and myths. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of penile anatomy, function, and performance, aiming to demystify and educate. From its biological significance to the intricacies of its structure and the factors influencing its performance, we aim to provide an insightful and informative journey into the world of the penis.
The Anatomy of the Penis: A Complex Structure

The penis is an external male genitalia, a vital part of the reproductive system, and serves both urinary and reproductive functions. Its structure is intricate, designed to perform a range of tasks, from urine excretion to sexual intercourse and reproduction. Let’s explore its anatomy and the roles of its various components.
External Structure
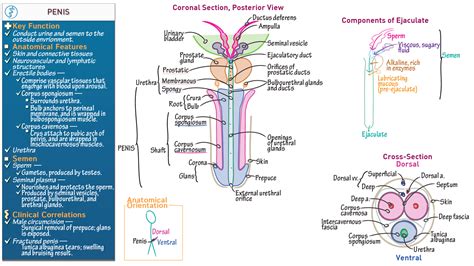
The penis is typically divided into three main parts: the root, body, and glans. The root, or radix, is the part of the penis that is attached to the pubic bone. It is a hidden structure, not visible externally. The body, or corpus, is the shaft of the penis, which is made up of three cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue known as the corpus cavernosum and the corpus spongiosum. The glans, or glans penis, is the cone-shaped head of the penis, which is typically smooth and sensitive.
The penis also features the foreskin, or prepuce, a retractable double-layered fold of skin that covers the glans. In circumcised males, this foreskin is removed. Additionally, the urethral opening, located at the tip of the glans, allows for the passage of urine and semen.
Internal Anatomy
Internally, the penis is composed of a complex network of tissues, nerves, and blood vessels. The corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum are filled with spongy erectile tissue, which becomes engorged with blood during an erection. The corpus cavernosum is responsible for the majority of the penis’ length and width during an erection, while the corpus spongiosum surrounds the urethra and is responsible for maintaining rigidity at the tip of the penis.
The penis is also richly innervated with sensory nerves, making it highly sensitive to touch and stimulation. The dorsal nerve of the penis is a crucial component, providing sensory innervation to the glans and body of the penis.
| Penile Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Root (Radix) | Anchors the penis to the pubic bone |
| Body (Corpus) | Provides length and width during an erection |
| Glans | Highly sensitive structure, crucial for sexual pleasure |
| Foreskin (Prepuce) | Protects the glans and can enhance sexual pleasure |
| Urethral Opening | Allows for the passage of urine and semen |

Penile Performance: Factors and Mechanics
Penile performance is a multifaceted concept, influenced by a range of physical, psychological, and environmental factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing penile health and function.
The Erection Process
An erection is a complex physiological process, involving a series of events that lead to the swelling and rigidity of the penis. It is primarily driven by the relaxation of smooth muscles and the influx of blood into the penis.
The process begins with nerve signals from the brain, which stimulate the release of nitric oxide in the penis. Nitric oxide acts as a vasodilator, causing the smooth muscles in the corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum to relax. This relaxation allows blood to flow into the erectile tissue, filling the spaces and causing the penis to become erect.
During an erection, the blood pressure within the penis can reach up to 100-120 mmHg, significantly higher than the pressure in the systemic circulation. This high pressure is maintained by the compression of venous outflow from the penis, ensuring the blood remains trapped and the erection is sustained.
Factors Influencing Penile Performance
Numerous factors can impact penile performance, both positively and negatively. These include:
- Age: As men age, penile function can decrease due to a decline in testosterone levels and general vascular health.
- Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity can affect blood flow and nerve function, leading to erectile dysfunction.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle can negatively impact penile health and performance.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can all contribute to erectile dysfunction by affecting nerve signals and blood flow.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as antidepressants and blood pressure drugs, can have side effects that impact penile function.
Optimizing Penile Health and Performance
Maintaining penile health and optimizing performance involves a holistic approach, addressing physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors. Here are some strategies to consider:
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a significant impact on penile health. This includes:
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for erectile dysfunction. Quitting can improve blood flow and overall penile health.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support cardiovascular health and penile function.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve blood flow, reduce stress, and enhance overall penile health.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can impair penile function. Moderation is key.
Medical Interventions
In cases of erectile dysfunction, medical interventions may be necessary. These can include:
- Oral Medications: Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, such as Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra, can help improve blood flow to the penis.
- Injection Therapy: Injections of prostaglandin E1 directly into the penis can stimulate an erection.
- Vacuum Devices: These devices create suction, drawing blood into the penis to induce an erection.
- Penile Implants: For severe cases of erectile dysfunction, penile implants can provide a permanent solution.
Psychological Support
Psychological factors play a significant role in penile performance. Addressing stress, anxiety, and depression through counseling or therapy can have a positive impact on penile function.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the penis function during intercourse?
+During intercourse, the penis becomes erect due to the relaxation of smooth muscles and the influx of blood into the erectile tissue. This erection provides the necessary rigidity for penetration and sexual pleasure.
What is the average size of a penis?
+The average erect penis length is around 5.1 to 7.1 inches (13 to 18 cm), with a girth of approximately 4.7 to 5.1 inches (12 to 13 cm) in circumference. It’s important to note that penis size does not correlate with sexual performance or satisfaction.
Can erectile dysfunction be prevented?
+While not all cases of erectile dysfunction can be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and addressing underlying health conditions can reduce the risk. Regular check-ups and early treatment can also be beneficial.
The penis is a remarkable organ, with a complex anatomy and function. Understanding its intricacies can lead to better penile health and sexual satisfaction. By adopting a holistic approach and addressing physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors, men can optimize their penile performance and overall sexual well-being.



