What Is Insurance Premium

Insurance premiums are a fundamental concept in the world of insurance, serving as the financial cornerstone of risk management and protection. These premiums are the lifeblood of insurance companies, representing the regular payments made by policyholders in exchange for the assurance of financial coverage against potential losses or damages.
Understanding insurance premiums is essential for anyone seeking to protect their assets, health, or livelihood. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of insurance premiums, exploring their definition, how they are calculated, the factors that influence their rates, and the various types of insurance premiums available. By the end of this article, readers will have a clear understanding of insurance premiums and their role in the insurance landscape.
The Definition of an Insurance Premium

An insurance premium is the amount of money an individual or entity pays to an insurance company to secure a specific level of coverage for a defined period. It is the price of the insurance policy, representing the cost of the protection and peace of mind the policy provides.
Insurance premiums are typically paid at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually. These payments ensure that the policyholder remains covered and that the insurance company can provide the promised benefits should an insured event occur. The premium is the price of the insurance contract, reflecting the level of risk the insurance company is willing to assume.
How Insurance Premiums are Calculated

The calculation of insurance premiums is a complex process that involves several key factors. Insurance companies use a variety of data and statistical models to determine the appropriate premium for each policy. Here’s a breakdown of the primary elements that influence premium rates:
Risk Assessment
The assessment of risk is a critical aspect of premium calculation. Insurance companies evaluate the likelihood of an insured event occurring and the potential cost of that event. For example, in auto insurance, factors such as the driver’s age, driving record, and the make and model of the car are considered. Similarly, in health insurance, an individual’s age, medical history, and lifestyle choices are assessed to determine the level of risk.
Statistical Data
Insurance companies rely on vast amounts of statistical data to inform their premium calculations. This data includes historical claim records, demographic information, and industry-specific trends. By analyzing this data, insurance providers can make informed predictions about the likelihood and cost of future claims.
Loss Ratio
The loss ratio is a key metric in insurance, representing the relationship between the premiums earned and the amount paid out in claims. A loss ratio of 100% indicates that the insurance company is breaking even, with the premiums collected exactly covering the claims paid out. Ratios above 100% suggest the company is paying out more in claims than it is taking in, while ratios below 100% indicate a profitable situation.
Inflation and Market Factors
Premiums are also influenced by broader economic factors, including inflation and market conditions. As the cost of goods and services rises, so too does the cost of providing insurance coverage. Additionally, market competition can drive premiums up or down, depending on the supply and demand dynamics in the insurance industry.
Types of Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums come in various forms, each designed to cater to specific needs and preferences. Understanding the different types of premiums can help individuals and businesses choose the most suitable insurance plan for their circumstances.
Fixed Premiums
Fixed premiums are the most common type of insurance premium. As the name suggests, these premiums remain constant throughout the duration of the policy. The policyholder pays the same amount at regular intervals, regardless of any changes in risk factors or claims history.
Level Premiums
Level premiums are a type of fixed premium that remains constant throughout the policy term. However, the premium amount is typically calculated based on the policyholder’s age or the age at which the policy was purchased. Level premiums are often used in life insurance policies, providing a predictable and stable payment structure.
Stepped Premiums
Stepped premiums, also known as increasing premiums, are designed to account for the rising cost of insurance coverage over time. These premiums start at a lower rate and gradually increase at predetermined intervals. Stepped premiums are commonly used in health and life insurance policies, where the risk of claims typically rises with age.
Community-Rated Premiums
Community-rated premiums are based on the average risk level of a specific group or community rather than the individual risk factors of policyholders. This type of premium is often used in group insurance plans, such as those offered by employers. Community-rated premiums can provide more affordable coverage for individuals with higher-than-average risk factors.
Individual-Rated Premiums
Individual-rated premiums, as the name implies, are calculated based on the specific risk factors of each individual policyholder. These premiums take into account personal characteristics, such as age, health status, driving record, and more. Individual-rated premiums are commonly used in personal insurance policies, such as auto and health insurance.
The Impact of Premiums on Insurance Coverage
The premium is a critical component of an insurance policy, as it directly impacts the level of coverage and benefits provided. In general, higher premiums tend to correspond with more comprehensive coverage and a wider range of benefits. Conversely, lower premiums may result in more limited coverage and exclusions.
For example, in health insurance, a higher premium might provide coverage for a broader range of medical services and prescriptions, while a lower premium might only cover essential care and exclude certain treatments or medications.
Additionally, premiums can influence the deductibles and copayments associated with an insurance policy. Higher premiums often come with lower deductibles and copayments, meaning policyholders pay less out of pocket when making claims. Lower premiums, on the other hand, may result in higher deductibles and copayments, shifting more of the financial burden onto the policyholder.
Managing Insurance Premiums
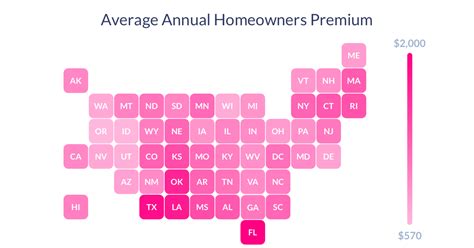
Managing insurance premiums is an important aspect of financial planning and risk management. Here are some strategies to consider when aiming to control and optimize insurance premiums:
Shop Around
Insurance rates can vary significantly between providers, so it’s essential to compare quotes from multiple companies. Shopping around can help you find the most competitive rates for your specific needs.
Bundle Policies
Many insurance companies offer discounts when you bundle multiple policies together. For example, combining your auto and home insurance policies with the same provider can result in substantial savings.
Review Your Coverage
Regularly reviewing your insurance coverage is crucial to ensure you’re not overpaying for unnecessary benefits. As your circumstances change, you may find that you no longer require certain types of coverage, allowing you to adjust your premiums accordingly.
Maintain a Good Risk Profile
Insurance companies reward policyholders who demonstrate responsible behavior and a low risk of claims. Maintaining a good driving record, a healthy lifestyle, or a secure home can all lead to lower premiums. Additionally, some insurance companies offer discounts for taking preventive measures, such as installing security systems or maintaining a healthy weight.
Consider Payment Plans
Many insurance companies offer flexible payment plans, allowing you to pay your premiums monthly or in installments. While this may result in slightly higher overall costs due to interest or administrative fees, it can make insurance more affordable by spreading out the payments.
Future Trends in Insurance Premiums
The insurance industry is constantly evolving, and premiums are no exception. Here are some trends that are likely to shape the future of insurance premiums:
Technology and Data Analytics
Advancements in technology and data analytics are enabling insurance companies to make more precise risk assessments. This can lead to more accurate premium calculations and potentially lower rates for policyholders. Additionally, the use of telematics in auto insurance and wearable devices in health insurance can provide real-time data, allowing for more dynamic and personalized premiums.
Risk Mitigation Programs
Insurance companies are increasingly focusing on risk mitigation as a way to reduce claims and, consequently, premiums. These programs can include incentives for policyholders to adopt safer behaviors or make improvements to their homes or vehicles to reduce the likelihood of accidents or losses.
Pay-As-You-Go Models
Pay-as-you-go insurance models, where premiums are based on actual usage rather than fixed rates, are gaining traction in certain industries. This approach is particularly relevant in auto insurance, where usage-based insurance (UBI) programs charge premiums based on factors such as mileage, driving behavior, and time of day.
Consumer Education
As consumers become more educated about insurance and the factors that influence premiums, they are better equipped to make informed choices. Insurance companies are likely to continue investing in consumer education to promote understanding and trust in the insurance process.
Regulatory Changes
Government regulations and policies can have a significant impact on insurance premiums. Changes in healthcare legislation, for example, can influence the cost of health insurance. Additionally, regulatory bodies may implement measures to promote competition and transparency in the insurance market, which can benefit consumers by driving down premiums.
Conclusion
Insurance premiums are a vital component of the insurance landscape, serving as the financial bridge between policyholders and the protection they seek. By understanding how premiums are calculated, the various types available, and the strategies for managing them, individuals and businesses can make more informed decisions about their insurance coverage. As the insurance industry continues to evolve, staying abreast of trends and developments will be key to navigating the complex world of insurance premiums.
How often do insurance premiums change?
+Insurance premiums can change annually or more frequently, depending on the insurance company and the type of policy. Factors such as changes in risk assessment, claims history, or market conditions can trigger premium adjustments.
Can I negotiate my insurance premium?
+While insurance premiums are typically non-negotiable, some companies may offer discounts or flexible payment plans. It’s worth inquiring about any available options to reduce your premium.
What happens if I can’t afford my insurance premium?
+If you’re struggling to afford your insurance premium, consider reaching out to your insurance provider to discuss payment plans or potential discounts. Some companies offer assistance programs for those facing financial hardship.
Are there any ways to lower my insurance premium without compromising coverage?
+Yes, there are several strategies to reduce your premium without sacrificing coverage. These include shopping around for better rates, bundling policies, maintaining a good risk profile, and taking advantage of any available discounts.



