Free Health Care Insurance
Health care is a fundamental right, and ensuring access to quality medical services without financial barriers is a goal that many nations strive to achieve. Free health care insurance, often referred to as universal health coverage, is a policy that aims to provide essential health services to all citizens without incurring significant financial hardship. In this article, we will delve into the concept of free health care insurance, exploring its benefits, challenges, and the impact it can have on individuals and societies.
Understanding Free Health Care Insurance

Free health care insurance, at its core, seeks to eliminate the financial barriers that prevent individuals from accessing necessary medical care. It is a system designed to ensure that everyone, regardless of their socioeconomic status, has equal opportunities to receive healthcare services when needed. This policy goes beyond traditional health insurance models, which often require premiums, deductibles, and copayments, creating a more inclusive and equitable healthcare system.
The concept of free health care insurance is grounded in the principle of social solidarity, where the costs of healthcare are shared across the population, often through general taxation. This approach aims to reduce the financial burden on individuals and families, especially during times of illness or injury when financial stability can be most vulnerable.
Key Features of Free Health Care Insurance
- Universal Coverage: Free health care insurance aims to provide coverage to all citizens, including those who may be underserved or face barriers in accessing traditional insurance plans. This ensures that everyone, from children to the elderly, has access to essential healthcare services.
- Comprehensive Benefits: The insurance typically covers a wide range of medical services, including primary care, hospitalization, prescription medications, mental health services, and preventive care. By offering comprehensive benefits, it encourages individuals to seek timely medical attention without fear of high costs.
- No Out-of-Pocket Expenses: One of the defining features of free health care insurance is the absence of out-of-pocket expenses for covered services. This means that individuals do not have to pay directly for medical treatments, consultations, or procedures, reducing the financial strain on households.
- Equitable Access: By removing financial barriers, free health care insurance promotes equitable access to healthcare. It ensures that individuals from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds, ethnicities, and geographical locations can access the same level of care, fostering a more inclusive society.
Implementing free health care insurance requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. Let's explore some of the key aspects and implications of this transformative policy.
Benefits of Free Health Care Insurance
Free health care insurance has the potential to bring about significant positive changes in the healthcare landscape. Here are some of the key benefits:
Improved Health Outcomes
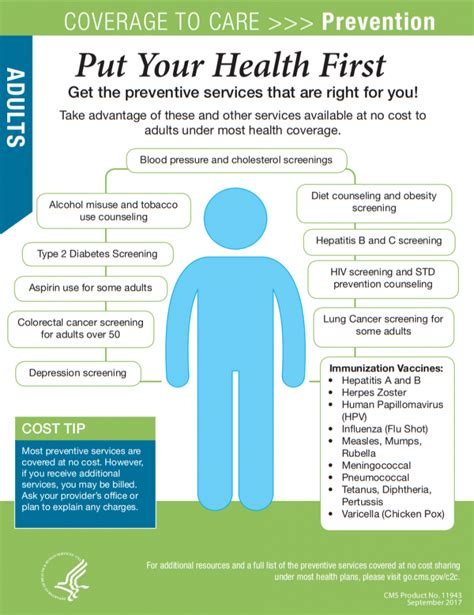
By removing financial barriers, free health care insurance encourages individuals to seek timely medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can lead to better health outcomes, as conditions are often more manageable when detected and addressed promptly. This proactive approach can reduce the severity of illnesses and improve overall population health.
Additionally, with comprehensive coverage, individuals are more likely to engage in preventive healthcare measures, such as regular check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings. Preventive care not only helps identify potential health issues but also promotes healthy lifestyles, ultimately reducing the burden of chronic diseases and improving long-term health.
Reduced Financial Burden
One of the most significant advantages of free health care insurance is the reduction of financial strain on individuals and families. Medical expenses can be a major source of financial stress, leading to debt, bankruptcy, and even poverty. By providing coverage without out-of-pocket expenses, the policy alleviates this burden, allowing individuals to focus on their health and well-being without the fear of overwhelming medical bills.
Enhanced Access to Quality Care
Free health care insurance aims to bridge the gap in access to quality healthcare services. It ensures that individuals from all walks of life, regardless of income or social status, can receive the same level of care. This inclusivity promotes a healthier society, as it reduces health disparities and ensures that everyone has an equal opportunity to achieve optimal health.
Increased Healthcare Utilization
With free health care insurance, individuals are more likely to utilize healthcare services when needed. This increased utilization can lead to better management of chronic conditions, improved disease control, and reduced complications. By encouraging regular healthcare visits, the policy contributes to a healthier and more resilient population.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of free health care insurance are compelling, implementing such a policy comes with its own set of challenges and considerations.
Funding and Sustainability
One of the primary challenges is securing sufficient funding to support the system. Free health care insurance relies on a robust funding mechanism, often through general taxation. This requires careful financial planning and management to ensure the long-term sustainability of the program. Governments and policymakers must strike a balance between providing comprehensive coverage and maintaining fiscal responsibility.
Healthcare Infrastructure
Expanding access to healthcare services also requires a well-developed healthcare infrastructure. This includes an adequate number of healthcare facilities, hospitals, and healthcare professionals to meet the increased demand. Investing in healthcare infrastructure is crucial to ensure that the system can effectively deliver quality care to all citizens.
Equitable Resource Allocation
Ensuring equitable access to healthcare services requires careful resource allocation. Policymakers must address potential disparities in healthcare delivery, ensuring that all regions and communities receive adequate resources. This includes addressing rural-urban disparities, providing access to specialized care, and promoting cultural sensitivity in healthcare practices.
Managing Demand
With free health care insurance, there may be an increase in demand for healthcare services. Managing this demand is crucial to maintain efficient healthcare delivery. Strategies such as promoting primary care, encouraging the use of telemedicine, and implementing healthcare triaging systems can help optimize resource utilization and ensure timely access to appropriate care.
Global Perspectives and Success Stories
Several countries around the world have successfully implemented free health care insurance models, showcasing the feasibility and positive outcomes of such policies. Let’s explore some notable examples:
United Kingdom: The National Health Service (NHS)
The United Kingdom’s National Health Service is a prime example of a successful free health care insurance system. Established in 1948, the NHS provides comprehensive healthcare services to all UK residents, free at the point of use. The system is funded through general taxation, ensuring equal access to healthcare for all citizens.
Canada: Medicare
Canada’s Medicare program offers universal health coverage to its citizens. The system, funded through a combination of federal and provincial taxes, provides access to a wide range of medical services, including physician services, hospital care, and some prescription medications. Canada’s Medicare system has been praised for its inclusivity and equitable access to healthcare.
New Zealand: The New Zealand Public Health System
New Zealand operates a publicly funded healthcare system, offering free or low-cost healthcare services to its residents. The system, known as the New Zealand Public Health System, covers a comprehensive range of services, including primary care, specialist consultations, and hospital treatments. New Zealand’s approach emphasizes prevention and community-based care, ensuring accessible and efficient healthcare.
Future Implications and Innovations

As the world continues to evolve, so do healthcare systems and policies. Here are some future implications and potential innovations in the realm of free health care insurance:
Digital Health Solutions
The integration of digital health technologies can enhance the efficiency and accessibility of free health care insurance systems. Telemedicine, digital health records, and mobile health applications can improve remote consultations, streamline administrative processes, and provide convenient access to healthcare services, especially in remote or underserved areas.
Preventive Care Initiatives
Emphasizing preventive care is a key strategy to reduce healthcare costs and improve population health. Free health care insurance systems can invest in initiatives that promote healthy lifestyles, such as nutrition and fitness programs, smoking cessation campaigns, and mental health awareness initiatives. By focusing on prevention, the need for costly treatments can be reduced, leading to a more sustainable healthcare system.
Personalized Medicine
Advances in genomics and precision medicine offer the potential to tailor healthcare interventions to individual needs. Free health care insurance systems can explore ways to integrate personalized medicine approaches, ensuring that treatments are targeted and effective. This precision-based healthcare can lead to improved outcomes and more efficient resource allocation.
Healthcare Data Analytics
Utilizing healthcare data analytics can help identify trends, predict disease outbreaks, and optimize resource allocation. Free health care insurance systems can leverage big data and artificial intelligence to improve healthcare delivery, identify inefficiencies, and develop targeted interventions. Data-driven decision-making can enhance the effectiveness and responsiveness of healthcare systems.
Conclusion
Free health care insurance is a transformative policy that has the potential to revolutionize healthcare systems, making them more inclusive, equitable, and accessible. By removing financial barriers, it ensures that individuals can focus on their health and well-being without the fear of financial hardship. While challenges exist, the benefits of free health care insurance, such as improved health outcomes, reduced financial burden, and enhanced access to quality care, make it a worthy pursuit for nations striving for a healthier and more resilient society.
What is the difference between free health care insurance and traditional health insurance?
+Free health care insurance differs from traditional health insurance in that it aims to provide coverage to all citizens without financial barriers. Traditional health insurance often requires premiums, deductibles, and copayments, creating financial hurdles for some individuals. Free health care insurance, on the other hand, is typically funded through general taxation, ensuring universal access to essential healthcare services.
How is free health care insurance funded?
+Free health care insurance is funded through various mechanisms, primarily general taxation. This means that the costs of healthcare are shared across the population, with governments and taxpayers contributing to the system. In some cases, additional funding may come from dedicated healthcare funds or specific taxes related to healthcare services.
Does free health care insurance cover all medical expenses?
+Free health care insurance typically covers a wide range of essential medical services, including primary care, hospitalization, and prescription medications. However, the specific benefits and coverage may vary depending on the country and its healthcare system. Some systems may have limitations or exclusions for certain services or treatments.



